Heaters
The benefits of infrared heating
Infrared heating has been around for a long time.
Since the dawn of the universe’s birth, the most efficient method of heat transfer has been through infrared rays.
Infrared heating is widely applicable, both for home and office, as well as for open and semi-closed areas, restaurants, terraces, rooms with huge volumes (difficult to heat with conventional heating), industrial warehouses and rooms, open halls and many others.
The field of application of infrared heating is unlimited.
How does it work?
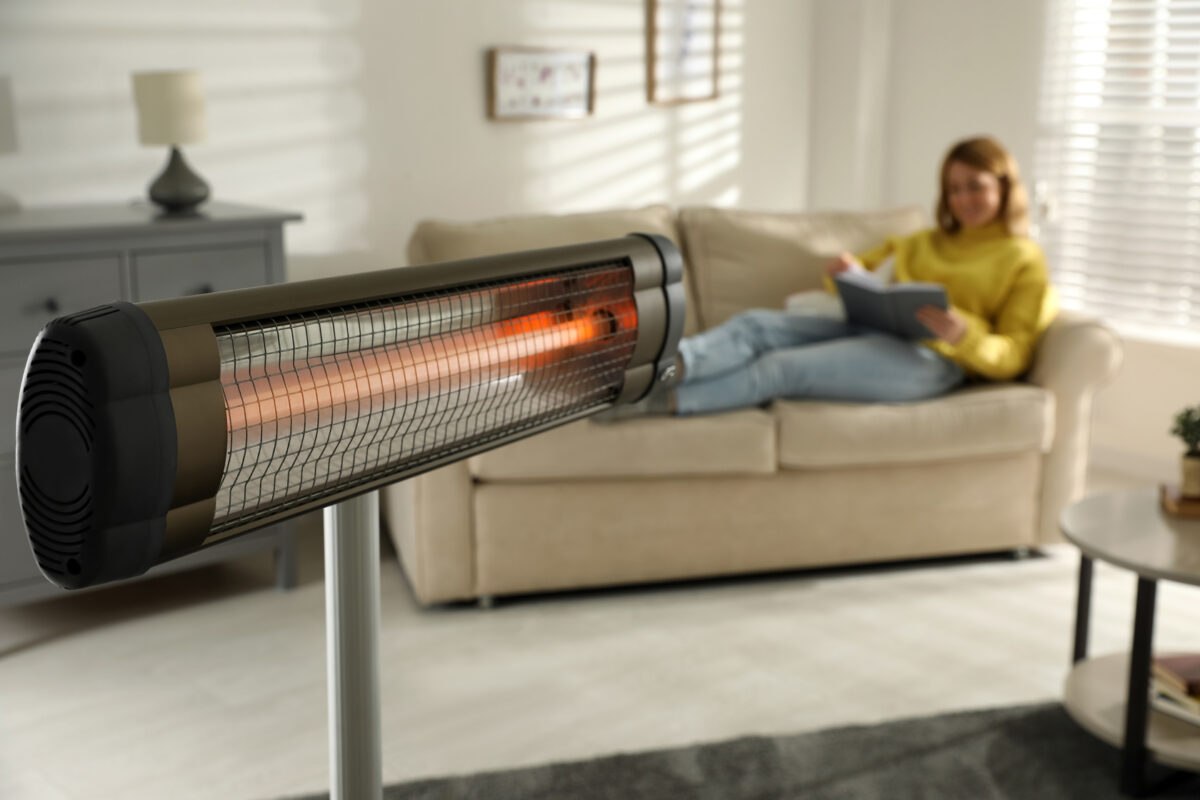
Infrared heating is a direct form of heating.
The heat source (the infrared emitter or lamp) emits: energy that is absorbed by the object directly from the emitter.
That is, thermal energy is not transferred through an intermediate medium.
This is one of the reasons for the high energy efficiency of infrared heating systems.
For example, conventional hot air heating must first heat the air, and then the air heats the object by convection.
Infrared energy is directed directly at the object.
Infrared energy is scattered from the source in the same way as visible light.
Exposed object surfaces easily absorb infrared energy and become warm.
Therefore, heating efficiency is related to the line between the source and the object.
The main argument for the effectiveness of infrared heating is the physical law , which states that: “The higher the temperature of a heat source, the greater the percentage of its infrared ( desired ) radiation and, respectively, the smaller the conventional ( unwanted ) share of heat release”. The main parameter giving us information about the efficiency of a heating system based on infrared radiation is the ratio of the infrared to the conventional share .
What exactly is infrared heat?
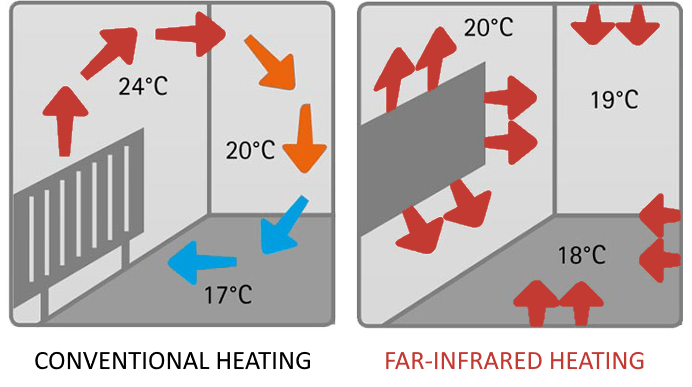
Infrared heat is a method of heating that, instead of heating the surrounding air, heats any object that the heat waves reach.
Let’s take sunlight as an example. The sun warms everything it touches with its rays. This, of course, does not mean that it will also heat the air. In winter, the wind remains cold, regardless of the fact that the day is sunny. The sun also shines during the winter months and we feel its warm rays, but at the same time we feel the cold gust of wind.
This is the main difference between infrared heating and other heating methods.
Infrared heating is a type of radiant energy that does not warm the surrounding air.
Application of infrared rays
Infrared rays are used in many fields.
They are used for massage, as heating with infrared rays pleasantly warms the skin and relaxes the muscles. Warmed muscles lead to relaxation of the body, which favors a long-lasting and effective massage.
Infrared radiation is widely used to transfer data between computers, portable devices, mobile devices and the like that are in close proximity to each other.
Infrared rays are also used very often in photography. In this way, it is possible to create images invisible to the human eye.
Thanks to infrared cameras and cameras, the parameters of buildings, rooms, various bodies and materials are examined.
Infrared radiation is also widely used in cosmetics.
With regular and prolonged exposure to infrared radiation, it greatly reduces the occurrence of skin problems, such as acne, dandruff, blackheads and others.
Heating is the main field in which infrared rays are used, due to the highly pronounced thermal effect.
Here we will look at infrared heating devices, which are divided into several main groups:
- Regarding the energy source they use – electric and gas.
- In relation to the temperature of the surface of the emitting object, respectively the wavelength
* long-wave – devices of this type are in the form of panels with a carbon heater, and the surface temperature is about 100ᴼC – 120ᴼC. Carbon is a material with exceptional elastic strength, lighter than steel by about 3-4 times, and by 35-40% than aluminum. Thanks to its properties, this type of heater has an extremely long service life – up to 100,000 hours of operation. Longwave panels are mainly used for domestic heating.
* short-wave – this type of infrared devices are in the form of radiant stoves with quartz lamps filled with various gases. The lamps are gold plated to prevent harmful radiation. The lamp surface temperature is 800ᴼC-900ᴼC. The service life of the lamps is 5000-10000 hours. They are used mainly in industrial and industrial heating, but they are increasingly used in households – summer gardens, verandas, semi-closed rooms, etc.
The advantages of infrared lamps are as follows:
*Extremely economical – 90% of energy is converted into heat
*Instant heating – giving off heat up to 1 second after switching on
*No noise, dust or smell
*Energy efficiency – 92%
*Glow/Emission – small, close to emissions from the Sun
*Main principle of heating – radiation